Angola
Republic of Angola
Population
38.98M
Area
1,246,700 km²
GDP
$80.40B
GDP Per Capita
$7,300
Pop. Density
31/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
KzAngolan kwanza(AOA)
Calling Code
+244
Timezone
UTC+01:00
Languages
Portuguese
Driving Side
right
Demonym
Angolan
Background
The Angolan National Revolution began in 1961, and in 1975, Angola won its independence when Portugal’s dictatorship fell, a collapse that occurred in part because of growing discontent over conflict in Angola and other colonies. Angola’s multiple independence movements soon clashed, with the Popular Movement for Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Agostinho NETO, taking power and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), led by Jonas SAVIMBI, emerging as its main competitor. After NETO’s death in 1979, Jose Eduardo DOS SANTOS, also of the MPLA, became president. Over time, the Angolan civil war escalated and became a major Cold War conflict, with the Soviet Union and Cuba supporting the MPLA and the US and South Africa supporting UNITA. Up to 1.5 million lives may have been lost -- and 4 million people displaced -- during the more than a quarter-century of fighting. SAVIMBI's death in 2002 ended UNITA's insurgency and cemented the MPLA's hold on power. DOS SANTOS did not seek reelection in 2017 and supported Joao LOURENCO’s successful bid to become president. LOURENCO was reelected in 2022. Angola scores low on human development indexes despite using its large oil reserves to rebuild since 2002.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑72.2% since 2006Population
↑89.3% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 64.6 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
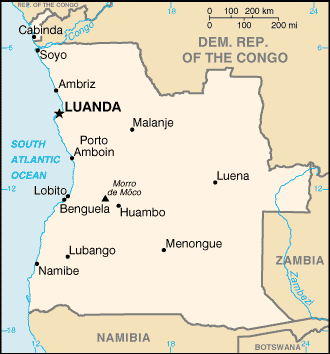
Geography20
Location
Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates
12 30 S, 18 30 E
Map references
Africa
Area
land: 1,246,700 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative
about eight times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Texas
Land boundaries
border countries: Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,646 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province); Republic of the Congo 231 km; Namibia 1,427 km; Zambia 1,065 km
Coastline
1,600 km
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate
semiarid in south and along coast to Luanda; north has cool, dry season (May to October) and hot, rainy season (November to April)
Terrain
narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to vast interior plateau
Elevation
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 1,112 m
Natural resources
petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, uranium
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
860 sq km (2014)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Indian Ocean drainage: Zambezi (1,332,412 sq km)
Internal (endorheic basin) drainage: Okavango Basin (863,866 sq km)
Major aquifers
Congo Basin, Upper Kalahari-Cuvelai-Upper Zambezi Basin
Population distribution
most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of Luanda
Natural hazards
locally heavy rainfall causes periodic flooding on the plateau
Geography - note
the province of Cabinda is an exclave, separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo
People & Society33
Population
male: 19,115,781
female: 19,869,015
Nationality
adjective: Angolan
Ethnic groups
Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, Mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22%
Languages
Portuguese 71.2% (official), Umbundu 23%, Kikongo 8.2%, Kimbundu 7.8%, Chokwe 6.5%, Nhaneca 3.4%, Nganguela 3.1%, Fiote 2.4%, Kwanhama 2.3%, Muhumbi 2.1%, Luvale 1%, other 3.6% (2014 est.)
Religions
Roman Catholic 41.1%, Protestant 38.1%, other 8.6%, none 12.3% (2014 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 50.7% (male 9,076,080/female 9,795,035)
65 years and over: 2.4% (2024 est.) (male 367,559/female 509,546)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 90 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 5.1 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 19.6 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 15.8 years
female: 16.8 years
Population growth rate
3.32% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
39.75 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
6.73 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
0.14 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
most people live in the western half of the country; urban areas account for the highest concentrations of people, particularly the capital of Luanda
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 4.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
9.292 million LUANDA (capital), 959,000 Lubango, 905,000 Cabinda, 809,000 Benguela, 783,000 Malanje (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.93 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.4 years (2015/16 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
183 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 60.7 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 50.3 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 60.8 years
female: 65.1 years
Total fertility rate
5.45 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
2.68 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 6.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.24 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Hospital bed density
0.8 beds/1,000 population (2019 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
8.2% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 3.78 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.72 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.27 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
57.2% (2016 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 30.3% (2016)
men married by age 18: 6% (2016)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 6.5% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 83.8% (2015 est.)
female: 51.9% (2015 est.)
Government23
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
former
etymology
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 8 50 S, 13 13 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings time
etymology: the Portuguese named the city São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda (Saint Paul of the Assumption of Loanda); over time, it was shortened to "Luanda," which may derive from a Bantu word meaning "tax" or "duty," in reference to local people paying their dues to the king of the Congo
Administrative divisions
Legal system
civil legal system based on Portuguese civil law; no judicial review of legislation
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one third of the National Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly subject to prior Constitutional Court review if requested by the president of the republic
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Angola
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
election results
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
legislature name
legislative structure
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the president on recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, an 18-member body chaired by the president; judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges - 4 nominated by the president, 4 elected by National Assembly, 2 elected by Supreme National Council, 1 elected by competitive submission of curricula; judges serve single 7-year terms
subordinate courts: provincial and municipal courts
Political parties
Humanist Party of Angola or PHI
National Front for the Liberation of Angola or FNLA; note - party has two factions
National Union for the Total Independence of Angola or UNITA (largest opposition party)
Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola or MPLA; note- ruling party in power since 1975
Social Renewal Party or PRS
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
info@angola.org
https://angola.org/
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
Consularluanda@state.gov
https://ao.usembassy.gov/
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CPLP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OAS (observer), SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, Union Latina, UNOOSA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
11 November 1975 (from Portugal)
National holiday
Independence Day, 11 November (1975)
Flag
meaning: red stands for liberty and black for the African continent; the emblem symbolizes workers and peasants
National symbol(s)
National color(s)
red, black, yellow
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Manuel Rui Alves MONTEIRO/Rui Alberto Vieira Dias MINGAO
history: adopted 1975
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Mbanza-Kongo
Economy32
Economic overview
middle-income, oil-dependent African economy; widespread poverty; rising inflation and currency depreciation; seeking diversification through agricultural production; significant corruption in public institutions; major infrastructure investments from China and US; exited OPEC in 2023
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $266.452 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $263.61 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 1.1% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 3% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $7,300 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $7,400 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$80.397 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 13.6% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 21.4% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 44.2% (2024 est.)
services: 39.3% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
cassava, bananas, maize, sweet potatoes, sugarcane, tomatoes, pineapples, onions, potatoes, citrus fruits (2023)
Industries
petroleum; diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, feldspar, bauxite, uranium, and gold; cement; basic metal products; fish processing; food processing, brewing, tobacco products, sugar; textiles; ship repair
Industrial production growth rate
5% (2024 est.)
Labor force
15.961 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 14.6% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 14.7% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 30.2% (2024 est.)
female: 25.7% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
32.3% (2018 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.4% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 39.6% (2018 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 0% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 0% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $13.871 billion (2019 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
10.1% (of GDP) (2019 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: $4.185 billion (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: $11.763 billion (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $36.961 billion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $50.12 billion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
China 40%, India 9%, UAE 6%, Spain 6%, Netherlands 5% (2023)
Exports - commodities
crude petroleum, diamonds, natural gas, ships, refined petroleum (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $23.688 billion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $28.564 billion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
China 19%, Portugal 10%, UAE 7%, India 6%, USA 5% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, wheat, ships, cars, trucks (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $13.942 billion (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $13.655 billion (2022 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy7
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 76.2%
electrification - rural areas: 7.3% (2018 est.)
Electricity
consumption: 16.214 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.725 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 2.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 74% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 121,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 7.783 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 1.244 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 4.928 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 343.002 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2024 est.) less than 1
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 70 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned media dominate; only four privately owned newspapers still exist in print form; state-run Radio Nacional de Angola (RNA) is the only outlet to offer programs in local languages such as Bantu; private stations operate in cities, including Catholic Radio Ecclesia, but RNA is the only radio broadcaster with near-national coverage (2023)
Internet country code
.ao
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
D2
Airports
107 (2025)
Heliports
2 (2025)
Railways
narrow gauge: 2,638 km (2022) 1.067-m gauge
Merchant marine
by type: general cargo 13, oil tanker 8, other 43
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security6
Military and security forces
Ministry of Interior: National Police, Border Guard Police (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 1.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.2% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 1.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 100,000 active duty Armed Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
most Angolan military weapons and equipment are of Russian or Soviet-era origin; there are smaller quantities of items originating from such suppliers as China, Brazil, Israel, Italy, South Africa, and the UAE (2025)
Military service age and obligation
20-45 years of age for compulsory and 18-45 years for voluntary military service for men; 20-45 years of age for voluntary service for women; 24-month conscript service obligation; the Navy is entirely staffed with volunteers (2025)
Military - note
the Angolan Armed Forces were created in 1991 under the Bicesse Accords signed between the Angolan Government and the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA); the current force is responsible for country’s external defense but also has some domestic security responsibilities, such as border protection; it participates in multinational exercises, as well as regional peacekeeping operations, including the deployment of several hundred troops to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 2023; in recent years, the military has placed additional emphasis on maritime security and protecting offshore resources (2025)
Transnational Issues1
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 75,308 (2024 est.)
