Cambodia
Kingdom of Cambodia
Population
17.23M
Area
181,035 km²
GDP
$46.35B
GDP Per Capita
$7,000
Pop. Density
95/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
៛Cambodian riel(KHR)
Calling Code
+855
Timezone
UTC+07:00
Languages
Khmer
Driving Side
right
Demonym
Cambodian
Background
The 1991 Paris Agreements ended the country’s civil war and mandated democratic elections, which took place in 1993 and ushered in a period of multi-party democracy with a constitutional monarchy. King Norodom SIHANOUK was reinstated as head of state, and the Cambodian People's Party (CPP) and the royalist FUNCINPEC party formed a coalition government. Nevertheless, the power-sharing arrangement proved fractious and fragile, and in 1997, a coup led by CPP leader and former PRK prime minister HUN SEN dissolved the coalition and sidelined FUNCINPEC. Despite further attempts at coalition governance, the CPP has since remained in power through elections criticized for lacking fairness, political and judicial corruption, media control, and influence over labor unions, all of which have been enforced with violence and intimidation. HUN SEN remained as prime minister until 2023, when he transferred power to his son, HUN MANET. HUN SEN has subsequently maintained considerable influence as the leader of the CPP and the Senate. The CPP has also placed limits on civil society, press freedom, and freedom of expression. Despite some economic growth and considerable investment from China over the past decade, Cambodia remains one of East Asia's poorest countries.
The remaining elements of the Khmer Rouge surrendered in 1999. A UN-backed special tribunal established in Cambodia in 1997 tried some of the surviving Khmer Rouge leaders for crimes against humanity and genocide. The tribunal concluded in 2022 with three convictions.
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑455.1% since 2006Population
↑29.3% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 70.7 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
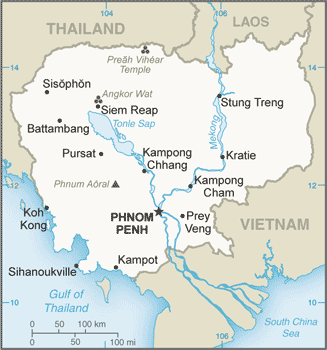
Geography20
Location
Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, between Thailand, Vietnam, and Laos
Geographic coordinates
13 00 N, 105 00 E
Map references
Southeast Asia
Area
land: 176,515 sq km
water: 4,520 sq km
Area - comparative
1.5 times the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Oklahoma
Land boundaries
border countries: Laos 555 km; Thailand 817 km; Vietnam 1158 km
Coastline
443 km
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
Climate
tropical; rainy, monsoon season (May to November); dry season (December to April); little seasonal temperature variation
Terrain
mostly low, flat plains; mountains in southwest and north
Elevation
lowest point: Gulf of Thailand 0 m
mean elevation: 126 m
Natural resources
oil and gas, timber, gemstones, iron ore, manganese, phosphates, hydropower potential, arable land
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
3,540 sq km (2012)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the southeast, particularly in and around the capital of Phnom Penh; further distribution is linked closely to the Tonle Sap and Mekong Rivers
Natural hazards
monsoonal rains (June to November); flooding; occasional droughts
Geography - note
a land of paddies and forests dominated by the Mekong River and Tonle Sap (Southeast Asia's largest freshwater lake)
People & Society36
Population
male: 8,362,224
female: 8,868,109
Nationality
adjective: Cambodian
Ethnic groups
Khmer 95.4%, Cham 2.4%, Chinese 1.5%, other 0.7% (2019-20 est.)
Languages
major-language sample(s):
សៀវភៅហេតុការណនៅលើពិភពលោក។ ទីតាំងពត៏មានមូលដានគ្រឹះយាងសំខាន់។. (Khmer)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Buddhist (official) 97.1%, Muslim 2%, Christian 0.3%, other 0.5% (2019 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 65.8% (male 5,456,941/female 5,765,206)
65 years and over: 5.3% (2024 est.) (male 323,591/female 584,257)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 42.9 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 8.4 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 11.9 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 26.9 years
female: 28.9 years
Population growth rate
0.95% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
17.74 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
5.62 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-2.62 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
population concentrated in the southeast, particularly in and around the capital of Phnom Penh; further distribution is linked closely to the Tonle Sap and Mekong Rivers
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 3.06% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
2.281 million PHNOM PENH (capital) (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.55 male(s)/female
total population: 0.94 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
23.3 years (2021-22 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
137 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 31.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 24.4 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 69.6 years
female: 73.3 years
Total fertility rate
2.14 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.05 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
0.21 physicians/1,000 population (2019)
Hospital bed density
0.7 beds/1,000 population (2018 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
3.9% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 4.12 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.41 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 24.9% (2025 est.)
female: 4.7% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
16.3% (2021 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
67.2% (2022 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 17.9% (2022)
men married by age 18: 3.3% (2022)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 11.6% national budget (2025 est.)
Literacy
male: 81.5% (2021 est.)
female: 63.6% (2021 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 11 years (2023 est.)
female: 11 years (2023 est.)
Government26
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
former
etymology
Government type
parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Capital
geographic coordinates: 11 33 N, 104 55 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name means "mountain of plenty," from the Cambodian words phnom (mountain or hill) and penh (full)
Administrative divisions
provinces: Banteay Meanchey, Battambang, Kampong Cham, Kampong Chhnang, Kampong Speu, Kampong Thom, Kampot, Kandal, Kep, Koh Kong, Kratie, Mondolkiri, Oddar Meanchey, Pailin, Preah Sihanouk, Preah Vihear, Prey Veng, Pursat, Ratanakiri, Siem Reap, Stung Treng, Svay Rieng, Takeo, Tbong Khmum
municipalities: Phnom Penh (Phnum Penh)
Legal system
civil law system (influenced by the UN Transitional Authority in Cambodia), customary law, Communist legal theory, and common law
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the monarch, by the prime minister, or by the president of the National Assembly if supported by one fourth of the Assembly membership; passage requires two-thirds majority of the Assembly membership; constitutional articles on the multiparty democratic form of government and the monarchy cannot be amended
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Cambodia
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister HUN MANET (since 22 August 2023)
cabinet: Council of Ministers named by the prime minister and appointed by the monarch
election/appointment process: monarch chosen by the 9-member Royal Council of the Throne from among all eligible males of royal descent; after legislative elections, a member of the majority party or majority coalition is named prime minister by the Chairman of the National Assembly and appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name
number of seats
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court and Constitutional Council judge candidates recommended by the Supreme Council of Magistracy, a 17-member body chaired by the monarch and includes other high-level judicial officers; judges of both courts appointed by the monarch; Supreme Court judges appointed for life; Constitutional Council judges appointed for 9-year terms with one third of the court renewed every 3 years
subordinate courts: Appellate Court; provincial and municipal courts; Military Court
Political parties
United National Front for an Independent, Neutral, Peaceful and Co-operative Cambodia (FUNCINPEC)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 4530 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7742
FAX: [1] (202) 726-8381
email address and website:
camemb.usa@mfaic.gov.kh
https://www.embassyofcambodiadc.org/
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
ACSPhnomPenh@state.gov
https://kh.usembassy.gov/
International organization participation
ADB, ARF, ASEAN, CICA, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Independence
9 November 1953 (from France)
National holiday
Independence Day, 9 November (1953)
Flag
meaning: red and blue are traditional Cambodian colors
National symbol(s)
Angkor Wat temple, kouprey (wild ox)
National color(s)
red, blue
National coat of arms
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: CHUON NAT/F. PERRUCHOT and J. JEKYLL
history: adopted 1941, restored 1993; the anthem, based on a Cambodian folk tune, was restored after the defeat of the Communist regime
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Angkor; Temple of Preah Vihear; Sambor Prei Kuk; Koh Ker: Archaeological Site of Ancient Lingapora or Chok Gargyar; Cambodian Memorial Sites: From centres of repression to places of peace and reflection (c)
Economy29
Economic overview
one of the fastest growing Southeast Asian economies; rebounding tourism and clothing exports; substantial manufacturing and construction sectors; new trade agreements expanding agricultural markets; significant public debt; investing in new ports and roads
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $116.658 billion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $111.095 billion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: 5% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 5.1% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $6,700 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $6,500 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$46.353 billion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 5.3% (2022 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2021: 2.9% (2021 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 41.8% (2024 est.)
services: 35.6% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
cassava, rice, maize, sugarcane, vegetables, oil palm fruit, rubber, bananas, jute, pork (2023)
Industries
tourism, garments, construction, rice milling, fishing, wood and wood products, rubber, cement, gem mining, textiles
Industrial production growth rate
9.5% (2024 est.)
Labor force
9.904 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 0.3% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 0.3% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 0.7% (2024 est.)
female: 0.9% (2024 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.9% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 6.6% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 6.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $8.285 billion (2023 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
12.2% (of GDP) (2023 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: $552.346 million (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: -$7.582 billion (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $27.753 billion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $25.497 billion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
USA 36%, Germany 6%, China 6%, Japan 6%, Thailand 5% (2023)
Exports - commodities
garments, semiconductors, trunks and cases, footwear, gold (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $29.421 billion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $34.759 billion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
China 39%, Thailand 20%, Vietnam 12%, Singapore 6%, Indonesia 3% (2023)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, fabric, gold, plastic products, synthetic fabric (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $19.984 billion (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $17.801 billion (2022 est.)
Debt - external
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy6
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 99%
electrification - rural areas: 88%
Electricity
consumption: 16.998 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 5.096 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.882 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 5.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 38.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Coal
consumption: 4.39 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 4.36 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2024 est.) less than 1
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 116 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
mix of state-owned, joint public-private, and privately owned broadcast media; 27 TV stations, with most operating on multiple channels, including 1 state-operated station with multiple locations and 11 stations either jointly operated or privately owned, some with several locations; multi-channel cable and satellite systems; 84 radio stations, including 1 state-owned broadcaster with multiple stations and a mix of public and private broadcasters; one international broadcaster is available, as well as one TV station that is jointly run by China and the Ministry of Interior; several TV and radio operators broadcast online only (often via Facebook) (2019)
Internet country code
.kh
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2022 est.)
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
XU
Airports
12 (2025)
Heliports
1 (2025)
Railways
narrow gauge: 642 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge
Merchant marine
by type: container ship 2, general cargo 123, oil tanker 18, other 52
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Royal Cambodian Armed Forces (RCAF): Royal Cambodian Army, Royal Khmer Navy, Royal Cambodian Air Force, Royal Gendarmerie (Military Police); National Committee for Maritime Security (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2023: 1.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 2.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 2.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military Expenditures 2020: 2.3% of GDP (2020 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; estimated 200,000 Armed Forces, including Gendarmerie (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the RCAF is armed largely with older Chinese and Russian/Soviet origin armaments; in recent years it has received limited amounts of more modern equipment from several suppliers, particularly China (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18 is the legal minimum age for military service for men and women (2025)
Military deployments
340 Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 180 Lebanon (UNIFIL) (2025)
Military - note
the RCAF was re-established in 1993 under the first coalition government from the merger of the Cambodian Government’s military forces (Cambodian People’s Armed Forces) and the two non-communist resistance forces (Sihanoukist National Army, aka National Army for Khmer Independence, and the Khmer People's National Liberation Armed Forces); thousands of communist Khmer Rouge fighters began surrendering by 1994 under a government amnesty program and the last of the Khmer Rouge forces (National Army of Democratic Kampuchea) were demobilized or absorbed into the RCAF in 1999 (2025)
Transnational Issues2
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 2,526 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 75,000 (2024 est.)
