Germany
Federal Republic of Germany
Population
84.01M
Area
357,022 km²
GDP
$4.66T
GDP Per Capita
$62,800
Pop. Density
235/km²
Quick Facts
Currency
€euro(EUR)
Calling Code
+49
Timezone
UTC+01:00
Languages
German
Driving Side
right
Demonym
German
Background
Historical Trends
GDP (USD)
↑53.8% since 2006Population
↑1.4% since 2006Life Expectancy at Birth
Latest: 80.5 yearsData source: World Bank Open Data
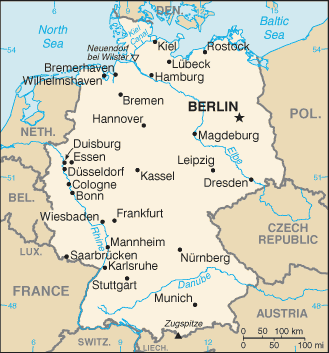
Geography20
Location
Central Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, between the Netherlands and Poland, south of Denmark
Geographic coordinates
51 00 N, 9 00 E
Map references
Europe
Area
land: 348,672 sq km
water: 8,350 sq km
Area - comparative
three times the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Montana
Land boundaries
border countries: Austria 801 km; Belgium 133 km; Czechia 704 km; Denmark 140 km; France 418 km; Luxembourg 128 km; Netherlands 575 km; Poland 447 km; Switzerland 348 km
Coastline
2,389 km
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate
temperate and marine; cool, cloudy, wet winters and summers; occasional warm mountain (foehn) wind
Terrain
lowlands in north, uplands in center, Bavarian Alps in south
Elevation
lowest point: Neuendorf bei Wilster -3.5 m
mean elevation: 263 m
Natural resources
coal, lignite, natural gas, iron ore, copper, nickel, uranium, potash, salt, construction materials, timber, arable land
Land use
agricultural land
agricultural land: arable land
agricultural land: permanent crops
agricultural land: permanent pasture
forest
other
Irrigated land
5,065 sq km (2020)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Stettiner Haff/Zalew Szczecinski (shared with Poland) - 900 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Population distribution
second most populous country in Europe; a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populations, particularly in the far-western part of the industrial state of North Rhine-Westphalia
Natural hazards
flooding
Geography - note
strategic location on North European Plain and along the entrance to the Baltic Sea; most major rivers in Germany -- the Rhine, Weser, Oder, Elbe -- flow northward; the Danube, which originates in the Black Forest, flows eastward
People & Society34
Population
male: 41,517,301
female: 42,494,983
Nationality
adjective: German
Ethnic groups
German 85.4%, Turkish 1.8%, Ukrainian 1.4%, Syrian 1.1%, Romanian 1%, Poland 1%, other/stateless/unspecified 8.3% (2022 est.)
Languages
major-language sample(s):
Das World Factbook, die unverzichtbare Quelle für grundlegende Informationen. (German)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Religions
Roman Catholic 24.8%, Protestant 22.6%, Muslim 3.7%, other 5.1%, none 43.8% (2022 est.)
Age structure
15-64 years: 62.5% (male 26,705,657/female 25,875,865)
65 years and over: 23.7% (2024 est.) (male 8,941,245/female 10,981,930)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 22.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 38.9 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 2.6 (2025 est.)
Median age
male: 45.5 years
female: 48.3 years
Population growth rate
-0.13% (2025 est.)
Birth rate
8.87 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Death rate
11.96 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
1.79 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population distribution
second most populous country in Europe; a fairly even distribution throughout most of the country, with urban areas attracting larger and denser populations, particularly in the far-western part of the industrial state of North Rhine-Westphalia
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.13% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Major urban areas - population
3.574 million BERLIN (capital), 1.788 million Hamburg, 1.576 million Munich, 1.144 million Cologne, 796,000 Frankfurt (2023)
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
29.9 years (2020 est.)
Maternal mortality ratio
4 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Infant mortality rate
male: 3.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
male: 79.6 years
female: 84.4 years
Total fertility rate
1.59 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.77 (2025 est.)
Drinking water source
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Health expenditure
Health expenditure (as % of national budget): 20.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
Physician density
4.53 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Hospital bed density
7.8 beds/1,000 population (2020 est.)
Sanitation facility access
improved: urban
improved: rural
improved: total
unimproved: urban
unimproved: rural
unimproved: total
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
22.3% (2016)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 5.57 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.97 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 19.4% (2025 est.)
female: 15% (2025 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
0.6% (2016 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
54.4% (2023 est.)
Education expenditure
Education expenditure (% national budget): 10.7% national budget (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 17 years (2023 est.)
female: 17 years (2023 est.)
Government26
Country name
conventional long form
conventional short form
local long form
local short form
former
etymology
Government type
federal parliamentary republic
Capital
geographic coordinates: 52 31 N, 13 24 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the origin of the name is unclear but may be related to the Old Slavic (Polabian) word berl or birl, meaning "swamp" and referring to the original settlement site by the Spree River
Administrative divisions
Legal system
civil law system
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by Parliament; passage and enactment into law require two-thirds majority vote by both the Bundesrat (upper house) and the Bundestag (lower house) of Parliament; articles including those on basic human rights and freedoms cannot be amended
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a German citizen or a resident alien who has lived in Germany at least 8 years
dual citizenship recognized: yes, but requires prior permission from government
residency requirement for naturalization: 8 years
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal; age 16 for some state and municipal elections
Executive branch
chief of state
head of government
cabinet
election/appointment process
most recent election date
chancellor: 6 May 2025
election results
2025: Friedrich MERZ (CDU) elected chancellor in second round; Federal Parliament vote - 325 to 289
2022: Frank-Walter STEINMEIER reelected president; Federal Convention vote count - Frank-Walter STEINMEIER (SPD) 1,045, Max OTTE (CDU) 140, Gerhard TRABERT (The Left) 96, Stefanie GEBAUER (Free Voters) 58, abstentions 86
expected date of next election
Legislative branch
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name
number of seats
electoral system
scope of elections
term in office
most recent election date
parties elected and seats per party
percentage of women in chamber
expected date of next election
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 69 (all appointed)
parties elected and seats per party: SPD 23; CDU 17; Green Party 15; Left Party 4; CSU 3; FW 3; FDP 2; other 2
percentage of women in chamber: 34.8%
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Federal Court of Justice judges selected by the Judges Election Committee, which consists of the Secretaries of Justice from each of the 16 federated states and 16 members appointed by the Federal Parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 65; half of Federal Constitutional Court judges are elected by the House of Representatives and half by the Senate; judges appointed for 12-year terms with mandatory retirement at age 68
subordinate courts: Federal Administrative Court; Federal Finance Court; Federal Labor Court; Federal Social Court; each of the 16 federated states or Land has its own constitutional court and a hierarchy of ordinary (civil, criminal, family) and specialized (administrative, finance, labor, social) courts; two English-speaking commercial courts opened in 2020 in the state of Baden-Wuerttemberg -- the Stuttgart Commercial Court and the Mannheim Commercial Court
Political parties
Alternative for Germany or AfD
Christian Democratic Union or CDU
Christian Social Union or CSU
Free Democratic Party or FDP
Free Voters or FW
The Left or Die Linke
Social Democratic Party or SPD
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission
chancery
telephone
FAX
email address and website
info@washington.diplo.de
https://www.germany.info/us-en
consulate(s) general
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission
embassy
Clayallee 170, 14191 Berlin (administrative services)
mailing address
telephone
FAX
email address and website
BerlinPCO@state.gov
https://de.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general
International organization participation
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS, CD, CDB, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNHRC, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMISS, UNOOSA, UNRWA, UNSOM, UNWTO, UPU, Wassenaar Arrangement, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Independence
18 January 1871 (establishment of the German Empire); divided into four zones of occupation (UK, US, USSR, and France) in 1945 after World War II; Federal Republic of Germany (FRG or West Germany) proclaimed on 23 May 1949 and included the former UK, US, and French zones; German Democratic Republic (GDR or East Germany) proclaimed on 7 October 1949 and included the former USSR zone; West Germany and East Germany unified on 3 October 1990, with all four powers formally relinquishing rights on 15 March 1991; notable earlier dates: 10 August 843 (Eastern Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire); 2 February 962 (crowning of OTTO I, recognized as the first Holy Roman Emperor)
National holiday
German Unity Day, 3 October (1990)
Flag
history: the colors can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor -- a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field
National symbol(s)
eagle
National color(s)
black, red, yellow
National coat of arms
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: August Heinrich HOFFMANN VON FALLERSLEBEN/Franz Joseph HAYDN
history: first adopted 1922; the anthem, also known as "Deutschlandlied" (Song of Germany), was originally adopted for its connection to the March 1848 liberal revolution; the Nazis later appropriated the first verse -- specifically the phrase "Deutschland, Deutschland ueber alles" (Germany, Germany above all) -- to promote nationalism, and the anthem was banned after 1945; in 1952, West Germany adopted the third verse as its national anthem; in 1990, it became the national anthem for the reunited Germany
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales:
Museumsinsel (Museum Island), Berlin (c); Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin (c); Speyer Cathedral (c); Aachen Cathedral (c); Bauhaus and its Sites in Weimar, Dessau, and Bernau (c); Caves and Ice Age Art in the Swabian Jura (c); Roman Monuments, Cathedral of St. Peter, and Church of Our Lady in Trier (c); Hanseatic City of Lübeck (c); Old Town of Regensburg with Stadtamhof (c); Würzburg Residence with the Court Gardens and Residence Square (c); Pilgrimage Church of Wies (c); Castles of Augustusburg and Falkenlust at Brühl (c); St Mary's Cathedral and St Michael's Church at Hildesheim (c); Abbey and Altenmünster of Lorsch (c); Maulbronn Monastery Complex (c); Collegiate Church, Castle and Old Town of Quedlinburg (c); Cologne Cathedral (c); Castle Church in Wittenberg (c); Classical Weimar (c); Wartburg Castle (c); Garden Kingdom of Dessau-Wörlitz (c); Monastic Island of Reichenau (c); Berlin Modernism Housing Estates (c); Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps (c); Moravian Church Settlements (c); Speicherstadt and Kontorhaus District with Chilehaus (c); The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier, an Outstanding Contribution to the Modern Movement (c); Archaeological Border complex of Hedeby and the Danevirke (c); Naumburg Cathedral (c); Mathildenhöhe Darmstadt (c); ShUM Sites of Speyer, Worms and Mainz (c); The Great Spa Towns of Europe (c); Jewish-Medieval Heritage of Erfurt (c); Schwerin Residence Ensemble (c); The Palaces of King Ludwig II of Bavaria: Neuschwanstein, Linderhof, Schachen and Herrenchiemsee (c); The Palaces of King Ludwig II of Bavaria: Neuschwanstein, Linderhof, Schachen and Herrenchiemsee (c)
Economy31
Economic overview
leading export-driven, core EU and eurozone economy; key automotive, chemical, engineering, finance, and green energy industries; growth stalled by energy crisis and declining exports; tight labor market with falling working-age population; fiscal rebalancing with phaseout of energy price supports
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2023: $5.26 trillion (2023 est.)
Real GDP (purchasing power parity) 2022: $5.274 trillion (2022 est.)
Real GDP growth rate
Real GDP growth rate 2023: -0.3% (2023 est.)
Real GDP growth rate 2022: 1.4% (2022 est.)
Real GDP per capita
Real GDP per capita 2023: $62,700 (2023 est.)
Real GDP per capita 2022: $62,900 (2022 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$4.66 trillion (2024 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2023: 5.9% (2023 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices) 2022: 6.9% (2022 est.)
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 25.8% (2024 est.)
services: 63.9% (2024 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption
government consumption
investment in fixed capital
investment in inventories
exports of goods and services
imports of goods and services
Agricultural products
milk, sugar beets, wheat, potatoes, barley, maize, rapeseed, pork, rye, triticale (2023)
Industries
iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, automobiles, food and beverages, shipbuilding, textiles
Industrial production growth rate
-3% (2024 est.)
Labor force
43.772 million (2024 est.)
Unemployment rate
Unemployment rate 2023: 3.1% (2023 est.)
Unemployment rate 2022: 3.2% (2022 est.)
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 7.4% (2024 est.)
female: 5.9% (2024 est.)
Population below poverty line
14.8% (2021 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.1% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 25% (2020 est.)
Remittances
Remittances 2023: 0.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
Remittances 2022: 0.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
Budget
expenditures: $1.369 trillion (2023 est.)
Public debt
Taxes and other revenues
11% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
Current account balance
Current account balance 2023: $251.479 billion (2023 est.)
Current account balance 2022: $161.759 billion (2022 est.)
Exports
Exports 2023: $1.958 trillion (2023 est.)
Exports 2022: $1.917 trillion (2022 est.)
Exports - partners
USA 10%, France 8%, Netherlands 7%, China 7%, Italy 6% (2023)
Exports - commodities
cars, vehicle parts/accessories, packaged medicine, plastic products, vaccines (2023)
Imports
Imports 2023: $1.781 trillion (2023 est.)
Imports 2022: $1.808 trillion (2022 est.)
Imports - partners
China 12%, Netherlands 7%, USA 7%, Poland 6%, France 5% (2023)
Imports - commodities
cars, vehicle parts/accessories, garments, natural gas, vaccines (2023)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2023: $322.7 billion (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold 2022: $293.914 billion (2022 est.)
Exchange rates
Currency
Exchange rates 2024
Exchange rates 2023
Exchange rates 2022
Exchange rates 2021
Exchange rates 2020
Energy8
Electricity access
Electricity
consumption: 519.691 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 60.316 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 69.353 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 25.774 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels
nuclear
solar
wind
hydroelectricity
biomass and waste
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 33 (2025)
Coal
consumption: 140.994 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.68 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 32.933 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 35.4 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 2.062 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 115.2 million barrels (2021 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 82.371 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 74.989 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 23.39 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Energy consumption per capita
Communications6
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2024 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 129 (2024 est.)
Broadcast media
a mix of publicly operated and privately owned TV and radio stations; 70 national and regional public broadcasters compete with nearly 400 privately owned national and regional TV stations; more than 90% of households have cable or satellite TV; hundreds of radio stations, including national and regional networks and a large number of local stations
Internet country code
.de
Internet users
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2023 est.)
Transportation6
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
D
Airports
840 (2025)
Heliports
449 (2025)
Railways
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 1, container ship 69, general cargo 82, oil tanker 32, other 411
Ports
total ports
large
medium
small
very small
ports with oil terminals
key ports
Military & Security7
Military and security forces
Federal Armed Forces (Bundeswehr): German Army (Deutsche Heer), German Navy (Deutsche Marine, includes naval air arm), German Air Force (Deutsche Luftwaffe, includes air defense), Cyber and Information Space (Cyber und Informationsraum) (2025)
Military expenditures
Military Expenditures 2024: 2% of GDP (2024 est.)
Military Expenditures 2023: 1.6% of GDP (2023 est.)
Military Expenditures 2022: 1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
Military Expenditures 2021: 1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 185,000 active-duty military personnel (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the inventory of Federal Armed Forces is comprised of weapons systems produced domestically or jointly with other European countries and Western imports, particularly from the US; Germany's defense industry is capable of manufacturing the full spectrum of air, land, and naval military weapons systems; it also participates in joint defense production projects with European partners and the US (2025)
Military service age and obligation
17-23 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women (must have completed compulsory full-time education and have German citizenship); service obligation 7-23 months or 12 years (2025)
Military deployments
up to 500 Iraq (NATO); 300 Kosovo (NATO/KFOR), Lebanon 170 (UNIFIL); up to 1,700 Lithuania (NATO) (2025)
Military - note
the Bundeswehr was established in 1955; at the height of the Cold War in the 1980s, it had nearly 600,000 personnel, over 7,000 tanks, and 1,000 combat aircraft; in addition, over 400,000 soldiers from other NATO countries—including about 200,000 US military personnel—were stationed in West Germany; in the years following the collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, the Bundeswehr shrank by more than 60% in size (over 90% in tanks and about 80% in aircraft), while funding fell from nearly 3% of GDP and over 4% of government spending in the mid-1980s to 1.2% and 1.6% respectively; by the 2010s, the Bundeswehr’s ability to fulfill its regional security commitments had deteriorated; the Russian annexation of Crimea in 2014 and full-scale assault on Ukraine in 2022 led to renewed emphasis on Germany’s leadership role in European defense and NATO and efforts to boost funding for the Bundeswehr to improve readiness, modernize, and expand (2025)
Transnational Issues2
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 100 (2023 est.)
stateless persons: 28,813 (2024 est.)
Illicit drugs
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
