Indian Ocean
Population
N/A
Area
70.56 km²
GDP
N/A
GDP Per Capita
N/A
Background
Geography13
Location
body of water between Africa, the Southern Ocean, Asia, and Australia
Geographic coordinates
20 00 S, 80 00 E
Area
Area - comparative
almost seven times the size of the US
Coastline
66,526 km
Climate
northeast monsoon (December to April), southwest monsoon (June to October); tropical cyclones occur during May/June and October/November in the northern Indian Ocean and January/February in the southern Indian Ocean
Ocean volume
percent of World Ocean total volume: 19.8%
Major ocean currents
the counterclockwise Indian Ocean Gyre comprised of the southward flowing warm Agulhas and East Madagascar Currents in the west, the eastward flowing South Indian Current in the south, the northward flowing cold West Australian Current in the east, and the westward flowing South Equatorial Current in the north; a distinctive annual reversal of surface currents occurs in the northern Indian Ocean; low atmospheric pressure over southwest Asia from hot, rising, summer air results in the southwest monsoon and southwest-to-northeast winds and clockwise currents, while high pressure over northern Asia from cold, falling, winter air results in the northeast monsoon and northeast-to-southwest winds and counterclockwise currents
Bathymetry
continental shelf
Exmouth Plateau
Indus Canyon
The Swatch of No Ground/Ganges Canyon (Bay of Bengal)
Sunda Shelf
continental slope
Bengal Fan
Indus Fan
abyssal plains
Arabian Basin
Crozet Basin
Madagascar Basin
Mid-Indian Basin
Mozambique Basin
Wharton Basin
mid-ocean ridge
Central Indian Ridge
Davie Ridge
Southeast Indian Ridge
Southwest Indian Ridge
undersea terrain features
Andaman-Nicobar Ridge
Chagos-Laccadive Ridge
Kerguelen Plateau
Madagascar Plateau
Mascarene Plateau
Mozambique Plateau
Ninetyeast Ridge
ocean trenches
Java/Sunda Trench (deepest point in the Indian Ocean)
atolls
Bassas da India
Chagos Archipelago/Diego Garcia
Europa Island
Juan de Nova Island
Lakshadweep Islands
Maldive Islands
Seychelles
Elevation
lowest point: Java Trench -7,192 m unnamed deep
mean depth: -3,741 m
ocean zones: the ocean is divided into three zones based on depth and light level; sunlight entering the water may travel about 1,000 m into the oceans under the right conditions, but there is rarely any significant light below 200 m
euphotic zone: the upper 200 m (656 ft) is also called "sunlight" zone; only a small amount of light penetrates beyond this depth
dysphotic zone: between 200 m (656 ft) and 1,000 m (3,280 ft), and also called the twilight zone; the intensity of light rapidly dissipates as depth increases, and photosynthesis is no longer possible
aphotic zone: below 1,000 m (3,280 ft) and also called the midnight zone; sunlight does not penetrate to these depths
Natural resources
oil and gas fields, fish, shrimp, sand and gravel aggregates, placer deposits, polymetallic nodules
Natural hazards
occasional icebergs pose navigational hazard in southern reaches
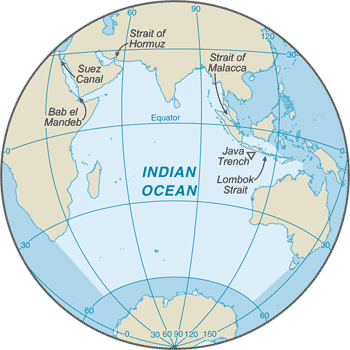
Geography - note
major chokepoints include Bab el Mandeb, Strait of Hormuz, Strait of Malacca, southern access to the Suez Canal, and the Lombok Strait
Government1
Country name
Compare Indian Ocean
See how Indian Ocean compares to other countries side by side.
Compare Countries